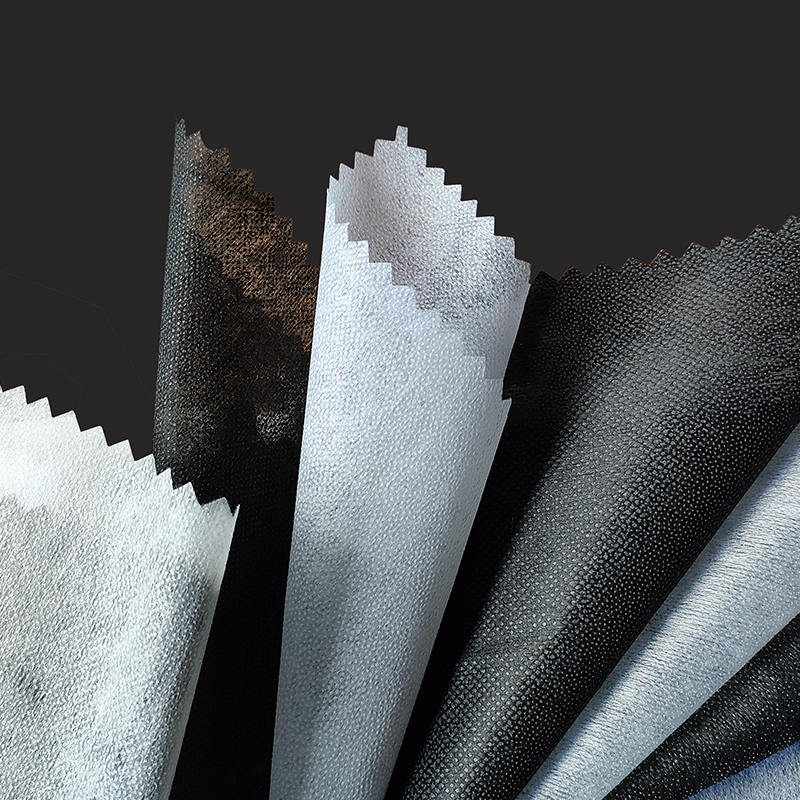
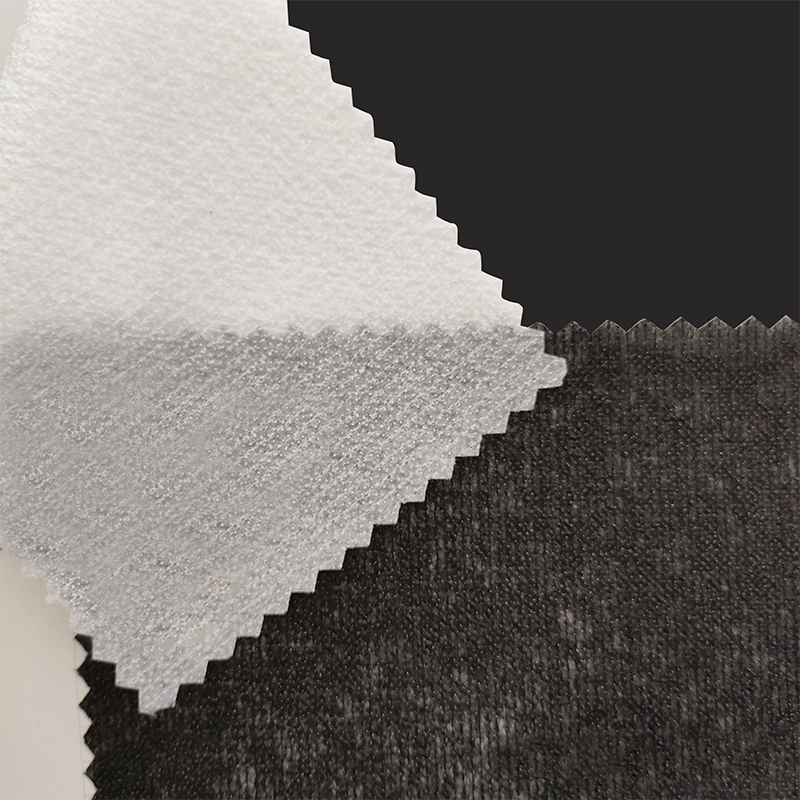
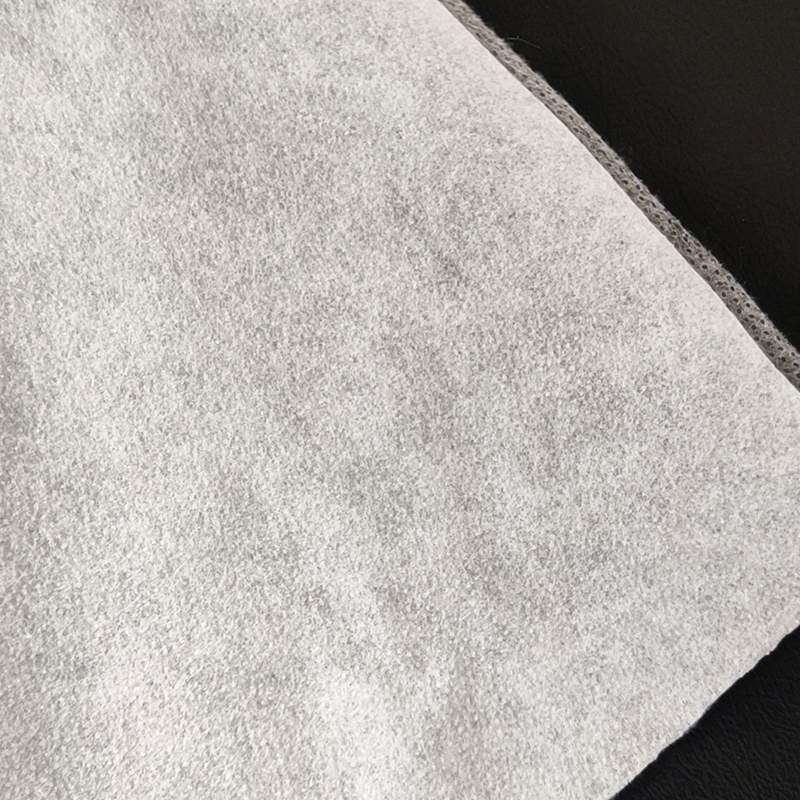
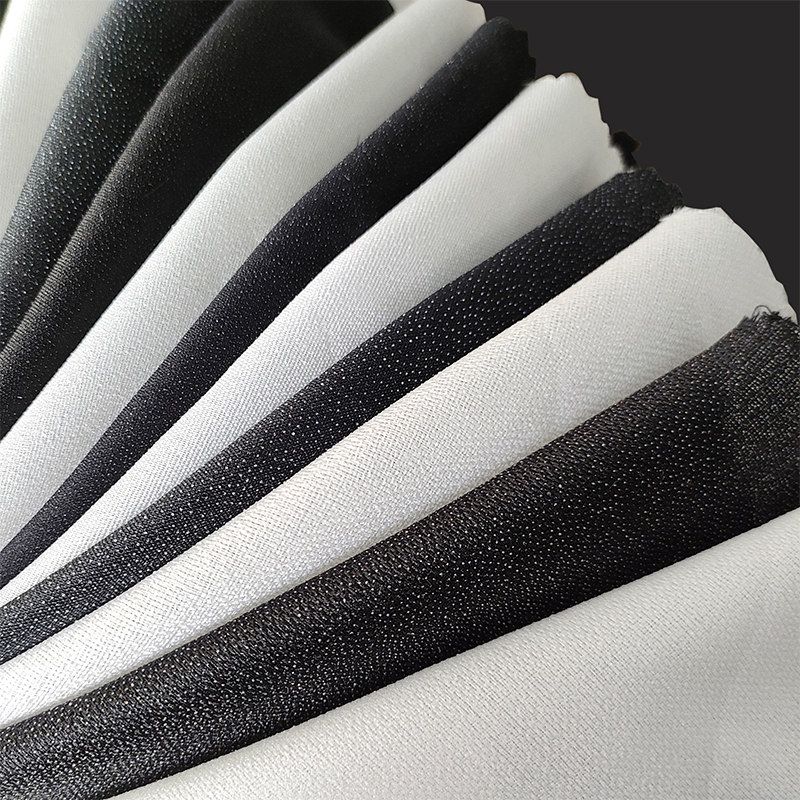
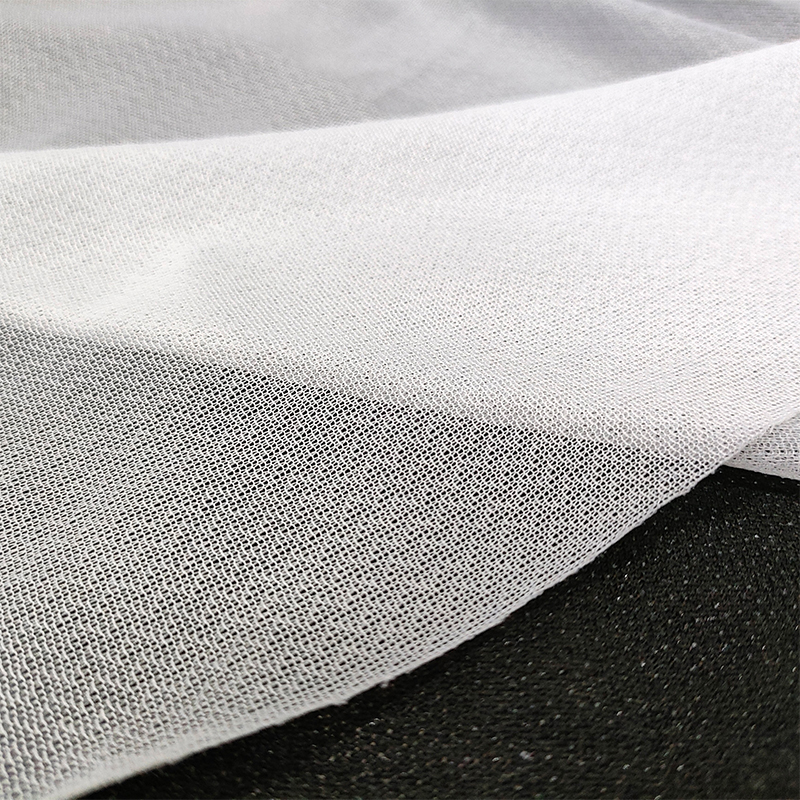
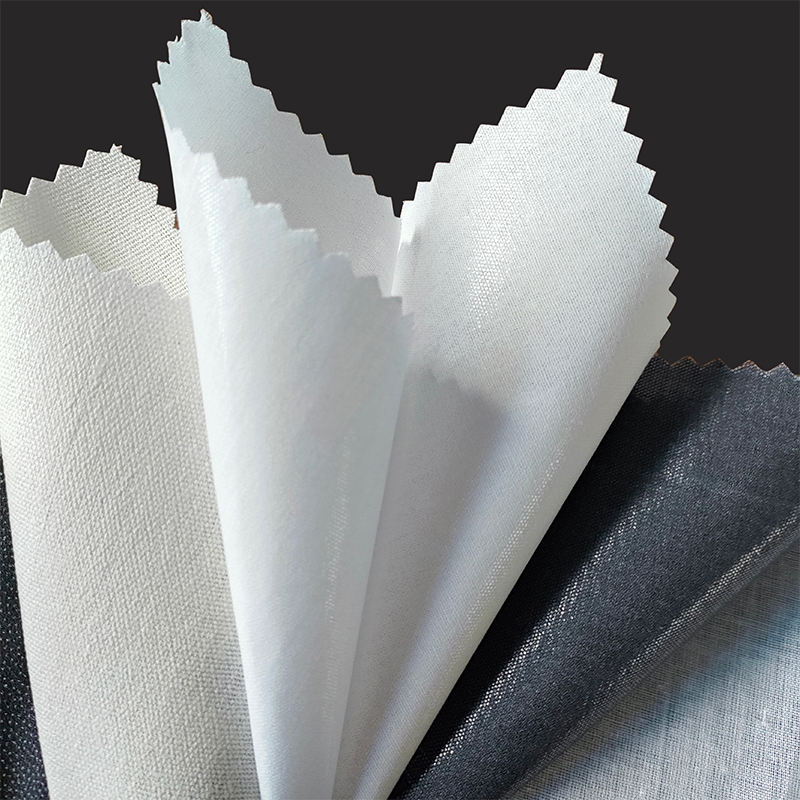
1. Raw materials of nonwoven fabric
Nonwoven fabric is mainly composed of polyester, polypropylene or viscose fibers. These fibers are light, strong, chemically resistant and have good processability, making them ideal materials for making nonwoven fabrics. Polyester fibers are usually used in applications that require durability and UV resistance, while polypropylene fibers are more suitable for disposable products and sanitary products due to their lighter weight and lower production costs. Viscose fibers are often used in medical and personal care products due to their good water absorption and skin-friendliness.
2. Mechanical forming process
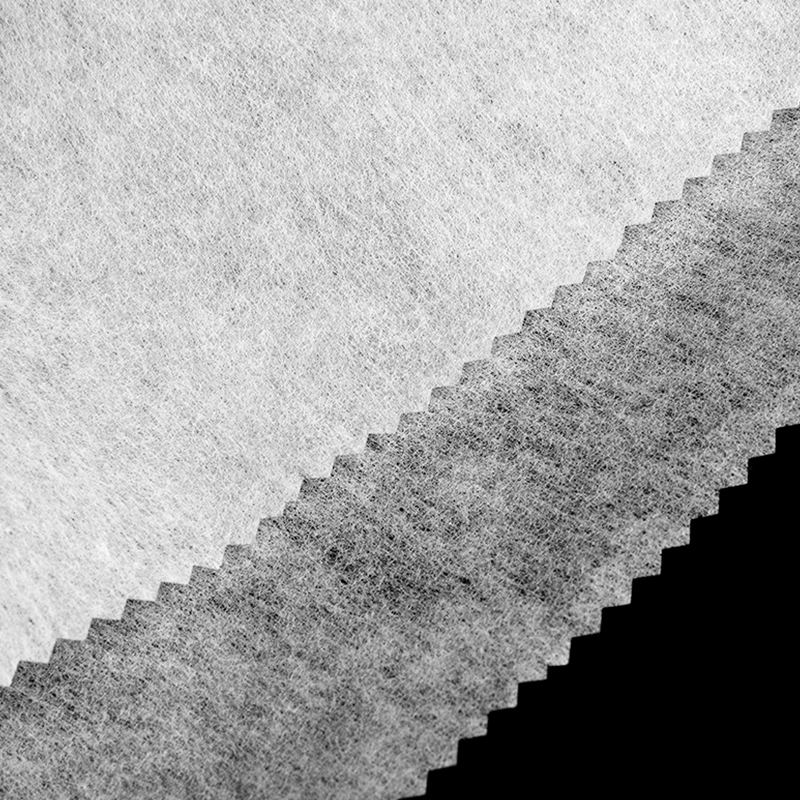
Mechanical forming process is an important method in the production of nonwoven fabrics. It forms the fiber web into a three-dimensional structure to give it good physical properties. Common mechanical forming methods include needle punching and hydroentanglement.
Needle punching: Needle punching nonwoven fabrics are made by repeatedly puncturing the fiber web through a needle plate with barbs, so that the fibers are entangled with each other to form a solid structure. This process does not require the use of chemical adhesives, so the non-woven fabrics produced have high environmental performance. Needle-punched non-woven fabrics are often used in automotive interiors, carpets, and filter materials because of their high strength and durability.
Hydroentanglement: Hydroentangled non-woven fabrics are made by spraying high-pressure water on the fiber web to entangle and fix the fibers. The non-woven fabrics produced by this process have a good feel and high flexibility, and are often used in medical and sanitary products such as wet wipes and surgical gowns.
The advantage of the mechanical forming process is that there is no need to add chemical adhesives, the physical properties of the finished product are relatively stable, and the production process is more environmentally friendly. However, its process equipment is relatively complex and has high requirements for the uniformity of the fiber web.
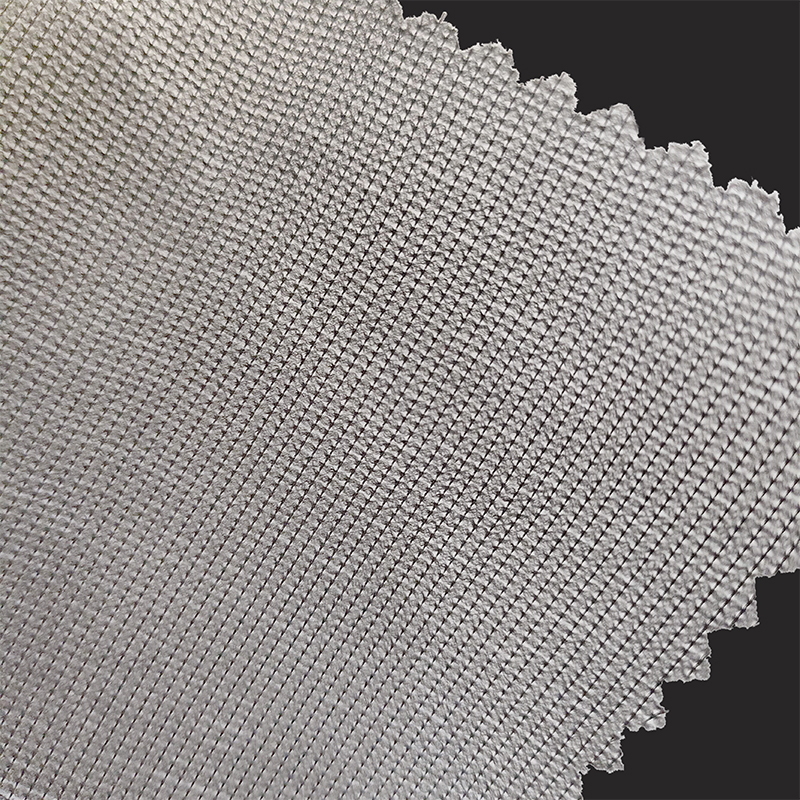
3. Chemical forming process
The chemical forming process is to immerse the fiber web in a chemical adhesive solution or spray a chemical adhesive to bond the fibers in the fiber web together to form a fabric with a certain strength. The chemical adhesives commonly used in this process include emulsion adhesives and solvent-based adhesives.
Emulsion adhesives: This adhesive is usually based on a polymer emulsion and can chemically react or physically entangle with the fibers in the fiber web to form a strong structure. The advantages of emulsion adhesives are that they are easy to handle and do not require the use of organic solvents during the production process, which meets environmental protection requirements.
Solvent-based adhesives: Solvent-based adhesives usually dissolve polymer adhesives so that they can be evenly distributed in the fiber web. As the solvent evaporates, the fiber web gradually solidifies and forms.
The advantages of the chemical molding process are fast production speed and the type and amount of adhesive can be adjusted according to different needs to achieve different performance requirements. However, the chemical molding process often uses a certain amount of chemicals, so it may not be suitable for application scenarios with high environmental protection requirements.
4. Thermal bonding process
In addition to mechanical and chemical molding processes, thermal bonding is also a common method for producing nonwoven fabrics. The thermal bonding process heats the fiber web to melt and bond the thermoplastic fibers together to form a backing fabric. Common thermal bonding processes include hot rolling and hot air.
Hot rolling method: The heated rollers are used to apply pressure to the fiber web to melt and bond the fibers together. Hot rolled nonwoven fabrics are often used in the production of disposable sanitary products such as diapers and sanitary napkins.
Hot air method: Hot air non-woven fabrics are made by blowing hot air through the fiber web, so that the fiber surface melts and bonds with each other. This non-woven fabric has a soft texture and is suitable for use as clothing lining, quilt filling, etc.

 English
English Español
Español Türk
Türk